Discover how Deep Bio’s DeepCDx Membrane IHC platform brings next-generation AI to immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis. Designed for tumor cell–specific precision, DeepCDx delivers subcellular insights by segmenting individual cells and quantifying membrane biomarker expression in detail.
Author: Deepbio
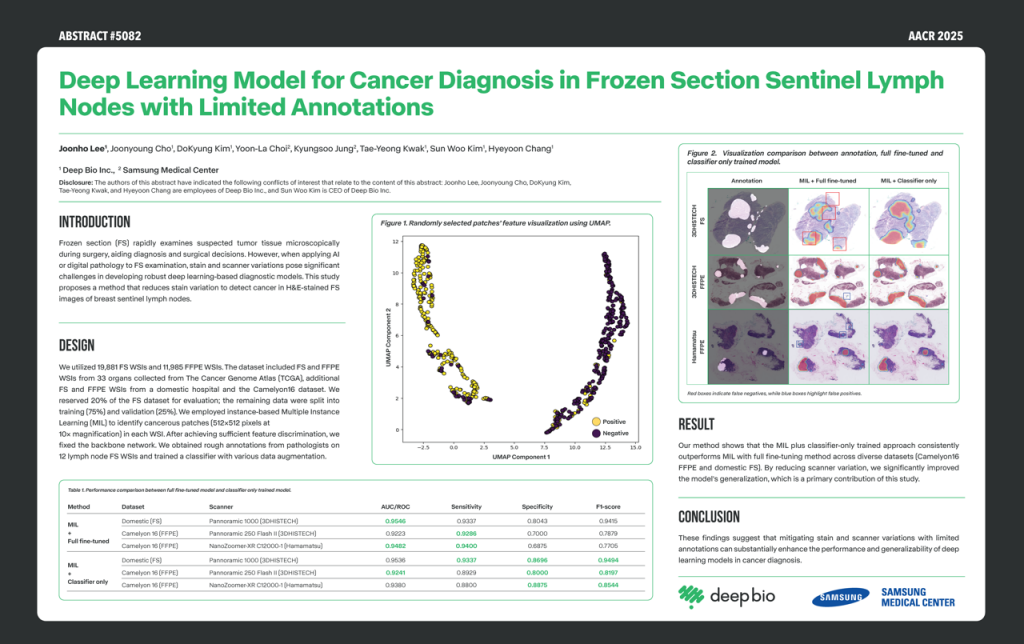
[Posters] AACR 2025 – Deep Learning Model for Cancer Diagnosis in Frozen Section Sentinel Lymph Nodes with Limited
Joonho Lee1, Joonyoung Cho1, DoKyung Kim1, Yoon-La Choi2, Kyungsoo Jung2, Tae-Yeong Kwak1, Sun Woo Kim1, Hyeyoon Chang1
1 Deep Bio Inc., 2 Samsung Medical Center
Disclosure: The authors of this abstract have indicated the following conflicts of interest that relate to the content of this abstract: Joonho Lee, Joonyoung Cho, DoKyung Kim,
Tae-Yeong Kwak, and Hyeyoon Chang are employees of Deep Bio Inc., and Sun Woo Kim is CEO of Deep Bio Inc.
This study aims to develop a deep-learning model for cancer diagnosis in frozen section sentinel lymph nodes with limited annotations. This study proposes a method to reduce stain and scanner variations using a multi-institutional dataset with multiple instance learning (MIL) approaches combined with a classifier-isolate training method. The proposed method outperforms the fine-tuned strategy.
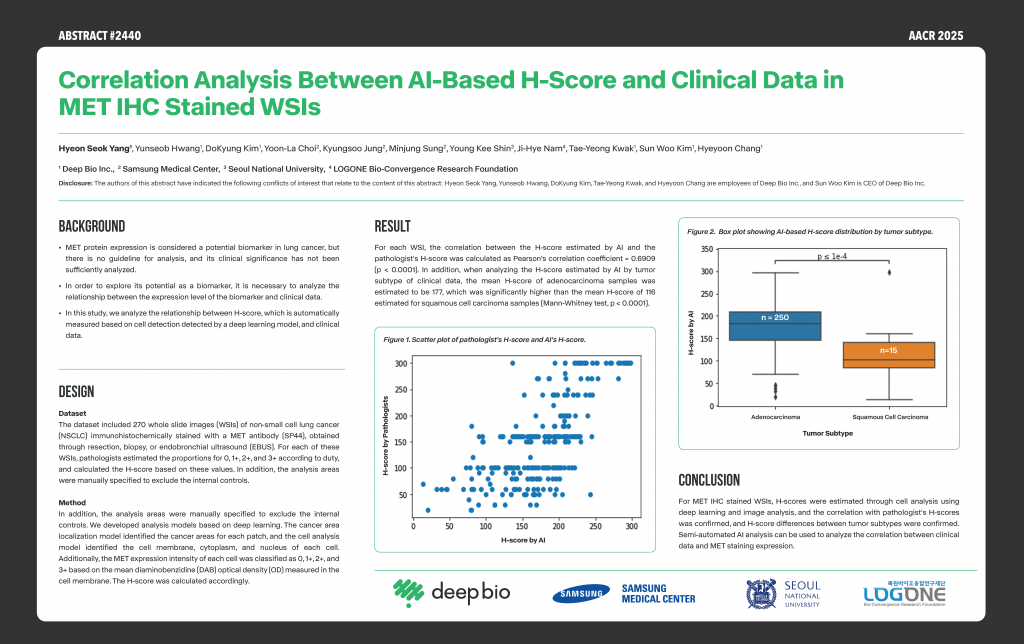
[Posters] AACR 2025 – Correlation analysis between AI-based H-score and clinical data in MET IHC stained WSIs
Hyeon Seok Yang1, Yunseob Hwang1, DoKyung Kim1, Yoon-La Choi2, Kyungsoo Jung2, Minjung Sung2, Young Kee Shin3, Ji-Hye Nam4, Tae-Yeong Kwak1, Sun Woo Kim1, Hyeyoon Chang1
1 Deep Bio Inc., 2 Samsung Medical Center, 3 Seoul National University, 4 LOGONE Bio-Convergence Research Foundation
Disclosure: The authors of this abstract have indicated the following conflicts of interest that relate to the content of this abstract: Hyeon Seok Yang, Yunseob Hwang, DoKyung Kim, Tae-Yeong Kwak, and Hyeyoon Chang are employees of Deep Bio Inc., and Sun Woo Kim is CEO of Deep Bio Inc.
This study confirmed the correlation between AI-estimated H-scores through cell analysis based on deep learning and image analysis and pathologist-estimated H-scores for MET IHC stained WSI, and compared the distribution of AI-estimated H-scores by tumor subtype.
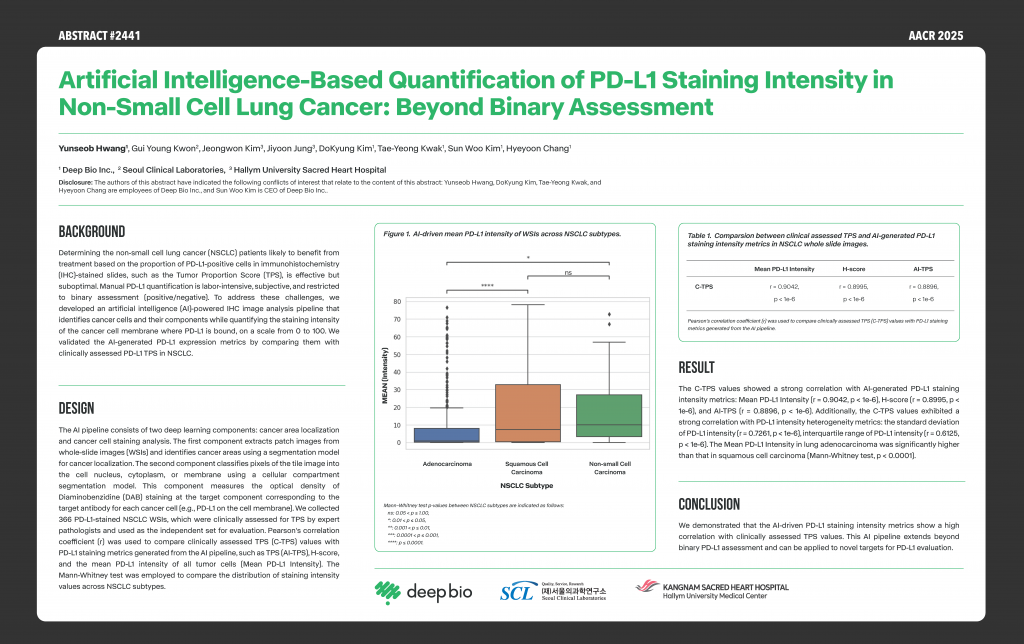
[Posters] AACR 2025 – Artificial intelligence-based quantification of PD-L1 staining intensity in non-small cell lung cancer: Beyond binary assessment
Yunseob Hwang1, Gui Young Kwon2, Jeongwon Kim3, Jiyoon Jung3, DoKyung Kim1, Tae-Yeong Kwak1, Sun Woo Kim1, Hyeyoon Chang1
1 Deep Bio Inc., 2 Seoul Clinical Laboratories, 3 Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital
Disclosure: The authors of this abstract have indicated the following conflicts of interest that relate to the content of this abstract: Yunseob Hwang, DoKyung Kim, Tae-Yeong Kwak,
and Hyeyoon Chang are employees of Deep Bio Inc., and Sun Woo Kim is CEO of Deep Bio Inc..
This research explores deep learning-based image analysis to quantify PD-L1 staining intensity in non-small cell lung cancer, demonstrating a strong correlation between AI-driven PD-L1 intensity and clinically assessed TPS values.
Deep Bio’s AI Algorithm Demonstrates Significant Prognostic Advancements in Prostate Cancer Study
– AI-derived tumor volume metrics enhance prognostic prediction over traditional pathology methods
SEOUL, SOUTH KOREA, April 8, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ — Deep Bio, a leader in AI-powered digital pathology, announced the publication of a groundbreaking study in Scientific Reports, an open-access journal from the Nature Publishing Group. Conducted in collaboration with Pusan National University College of Medicine, the study confirms the clinical value of Deep Bio’s AI algorithm in analyzing radical prostatectomy specimens at an unprecedented scale.
The study involved 992 prostate cancer patients and 29,646 digitized whole-slide images (WSIs) from radical prostatectomy specimens. It assessed the clinical feasibility and prognostic value of Deep Bio’s deep learning-based image analysis (DLIA) algorithm, DeepDx Prostate RP (Radical Prostatectomy). The algorithm demonstrated strong concordance with pathologists for Gleason grading. It outperformed manual assessments in tumor volume (TV) and percent tumor volume (PTV) measurements in predicting biochemical progression-free survival (BPFS).
Notably, when AI-derived PTV was incorporated into the CAPRA-S prognostic model, the predictive accuracy for recurrence was significantly improved (c-index increase, p=0.006). These findings highlight the algorithm’s potential to support clinical decision-making in prostate cancer management by offering consistent, quantitative insights.
“These findings validate our AI model’s ability to analyze prostate cancer at scale while improving prognostic accuracy,” said Sun Woo Kim, CEO of Deep Bio. “By integrating AI into digital pathology workflows, we are enabling more precise, data-driven decision-making that can lead to improved patient outcomes.”
This publication follows Deep Bio’s previous external validation study with Stanford University, published in BJU International, further establishing the global credibility of its AI-driven pathology solutions. The findings reinforce the role of AI in enhancing cancer diagnostics and prognosis prediction, paving the way for more widespread adoption of digital pathology tools in clinical practice.
About Deep Bio
Founded in 2015, Deep Bio Inc. develops AI-powered solutions for cancer pathology diagnostics, utilizing advanced deep learning technologies to enhance diagnostic precision and pathologist efficiency. The company specializes in in-vitro diagnostic medical device software (IVD SaMD) that integrates data-driven insights to support clinical decision-making.
Deep Bio’s flagship AI solution, DeepDx Prostate, marked with European CE-IVD, processes Whole Slide Images (WSI) to accurately identify and segment cancerous lesions. The software provides comprehensive classification by Gleason pattern, precise tumor localization, and critical metrics such as Gleason score quantification and tumor volume assessment, which are essential for diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment planning.
This AI technology enables detailed analysis and reporting, supporting healthcare professionals with precise diagnostic insights. In 2024, Deep Bio was recognized for its innovation with the CES Innovation Award. The company remains committed to transforming pathology workflows and improving patient outcomes worldwide.
[Peer-Reviewed Publications] Scientific Reports – Clinical Implications of Deep Learning- Based Image Analysis of Whole Radical Prostatectomy Specimens
Scientific Reports volume 15 (by Springer Nature)
Article number: 11006 (2025) | DOI:10.1038/s41598-025-95267-5
Published: 31 March 2025
Authors: Tae-Yeong Kwak, Chan Ho Lee, Won Young Park, Ja Yoon Ku, Chang Wook Jeong, Eu Chang Hwang, Seock Hwan Choi, Joonyoung Cho, Hyeyoon Chang, Kyung Hwan Kim, Byeong Jin Kang, Sun Woo Kim & Hong Koo Ha
Abstract
Prostate cancer (PCa) diagnosis faces significant challenges due to its complex pathological characteristics and insufficient pathologist resources. While deep learning-based image analysis (DLIA) shows promise in enhancing diagnostic accuracy, its application to radical prostatectomy (RP) specimens remains underexplored. In this study, we evaluated the clinical feasibility and prognostic value of a DLIA algorithm for Gleason grading and tumor quantification on whole RP specimens. Using 29,646 digitized H&E-stained slides from 992 patients who underwent RP, we compared the case-level algorithm results with pathologist assessments for the International Society of Urological Pathology grade groups (GG), tumor volumes (TV), and percent tumor volumes (PTV). We also evaluated their prognostic performance in predicting biochemical progression-free survival (BPFS). Pathologists identified cancer in 986 cases and assigned GG in 980, while the DLIA algorithm identified cancer and assigned GG to all cases without omission. DLIA-assigned GG showed fair concordance with pathologist assessments (linear-weighted Cohen’s kappa: 0.374) and demonstrated similar efficacy in predicting BPFS (c-index: 0.644 for DLIA vs. 0.654 for pathologists; p = 0.52). In tumor quantification, DLIA-measured TV and PTV were strongly correlated with pathologist-based measurements (Pearson’s correlation coefficient: 0.830 and 0.846, respectively), but showed stronger efficacy in BPFS prediction, with c-index values of 0.657 and 0.672 compared to 0.622 and 0.641, respectively. Incorporating DLIA-derived PTV into the CAPRA-S score significantly improved its predictive accuracy for BCR (p = 0.006), increasing the c-index from 0.704 to 0.715. Our findings indicate that DLIA algorithms can enhance the accuracy of Gleason grading and tumor quantification in RP specimens, providing valuable support in clinical decision-making for PCa management.
[AACR 2025] Deep Bio to Present Cutting-Edge AI-Powered Research in Digital Pathology at AACR 2025
AI-driven biomarker quantification and cancer diagnostics research to be featured in multiple poster presentations
SEOUL, SOUTH KOREA, April 2, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ — Deep Bio, a pioneer in AI-powered digital pathology, will present new research at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2025, highlighting the role of artificial intelligence in enhancing biomarker quantification and cancer diagnostics. The company’s findings will be showcased in multiple poster presentations based on deep learning models for PD-L1 and c-MET IHC quantification and frozen-section lymph node diagnosis.
The studies demonstrate how AI-driven image analysis can improve biomarker assessment, enhance patient stratification, and support clinical decision-making in oncology.
One featured study explores AI-based quantification of PD-L1 staining intensity in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The research reveals a strong correlation between AI-driven PD-L1 intensity scores and clinically assessed Tumor Proportion Scores (TPS), underscoring the potential of AI in enhancing precision and reproducibility in immunotherapy biomarker evaluation.
Another study investigates the application of AI-estimated H-scores in c-MET IHC-stained whole slide images (WSIs), demonstrating a high correlation with pathologist-assessed scores and analyzing biomarker expression across different tumor subtypes. Deep Bio’s AI technology provides precise, quantitative biomarker assessments by leveraging deep learning for fully quantitative biomarker assessment. It analyzes biomarker expression, cell morphology, and how they correlate with clinical data, offering new insights that could help identify novel biomarkers in the future.
Deep Bio will also present a novel deep-learning model for cancer diagnosis in frozen-section sentinel lymph nodes, designed to operate effectively even with limited annotations. By integrating multiple instance learning (MIL) and a classifier-isolate training approach, the AI model significantly improves diagnostic accuracy and robustness, outperforming conventional fine-tuned models. These findings highlight the potential of AI-driven pathology solutions to standardize and enhance frozen-section cancer diagnosis, a critical area in intraoperative decision-making.
Deep Bio’s proprietary DeepCDxⓇ Membrane IHC solution enables biomarker-agnostic, fully quantitative analysis that enhances biomarker interpretation and patient selection for targeted therapies. The company continues to push the boundaries of AI-powered pathology, offering cutting-edge solutions that drive precision medicine and accelerate drug development.
“These studies highlight the power of AI in cancer diagnostics,” said Sun Woo Kim, CEO of Deep Bio. “By applying deep learning to biomarker quantification and histopathology, we can deliver precise, reproducible insights—improving the assessment of PD-L1, c-MET, and frozen-section diagnostics to support better treatment decisions.”
Deep Bio’s research will be presented during the AACR Annual Meeting 2025, with details as follows:
Poster Presentation Details
1. Artificial intelligence-based quantification of PD-L1 staining intensity in non-small cell lung cancer: Beyond binary assessment
Session: Artificial Intelligence for Digital Pathology and Spatial Molecular Technologies
Date & Time: April 28, 2025 | 9:00 AM – 12:00 PM
Location: Poster Section 45, Board #26
Presenter: Tae-Yeong Kwak (Primary Author: Yunseob Hwang)
2. Correlation analysis between AI-based H-score and clinical data in MET IHC-stained WSIs
Session: Artificial Intelligence for Digital Pathology and Spatial Molecular Technologies
Date & Time: April 28, 2025 | 9:00 AM – 12:00 PM
Location: Poster Section 45, Board #25
Presenter: Tae-Yeong Kwak (Primary Author: Hyeon Seok Yang)
3. Deep Learning Model for Cancer Diagnosis in Frozen Section Sentinel Lymph Nodes with Limited Annotations
Session: Single-Cell and Spatial Molecular Analysis
Date & Time: April 29, 2025 | 9:00 AM – 12:00 PM
Location: Poster Section 47, Board #20
Presenter: Tae-Yeong Kwak (Primary Author: Joonho Lee)
For more information on Deep Bio’s AI-powered digital pathology solutions, visit www.deepbio.co.kr or booth #846
About Deep Bio
Founded in 2015, Deep Bio Inc. develops AI-powered solutions for cancer pathology diagnostics, utilizing advanced deep learning technologies to enhance diagnostic precision and pathologist efficiency. The company specializes in in-vitro diagnostic medical device software (IVD SaMD) that integrates data-driven insights to support clinical decision-making.
Deep Bio’s flagship AI solution, DeepDx Prostate, marked with European CE-IVD, processes Whole Slide Images (WSI) to accurately identify and segment cancerous lesions. The software provides comprehensive classification by Gleason pattern, precise tumor localization, and critical metrics such as Gleason score quantification and tumor volume assessment, which are essential for diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment planning.
This AI technology enables detailed analysis and reporting, supporting healthcare professionals with precise diagnostic insights. In 2024, Deep Bio was recognized for its innovation with the CES Innovation Award. The company remains committed to transforming pathology workflows and improving patient outcomes worldwide.
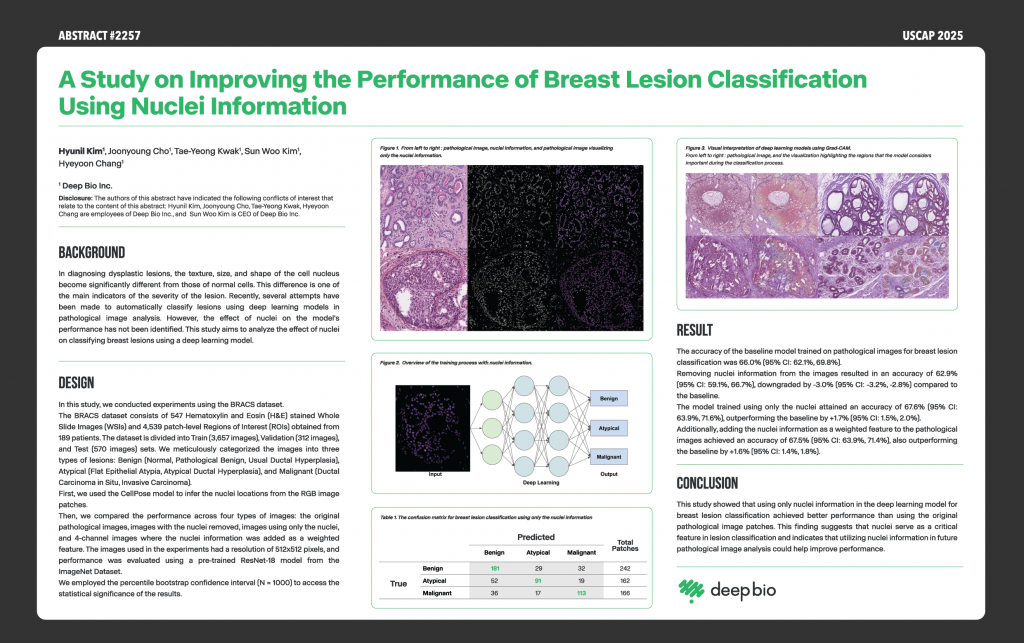
[Posters] USCAP 2025 – A Study on Improving the Performance of Breast Lesion Classification Using Nuclei Information
Hyunil Kim(1), Joonyoung Cho(1), Tae-Yeong Kwak(1), Sun Woo Kim(1), Hyeyoon Chang(1)
1 Deep Bio Inc.
Disclosure: The authors of this abstract have indicated the following conflicts of interest that relate to the content of this abstract: Hyunil Kim,
Joonyoung Cho, Tae-Yeong Kwak, Hyeyoon Chang are employees of Deep Bio Inc., and Sun Woo Kim is CEO of Deep Bio Inc.
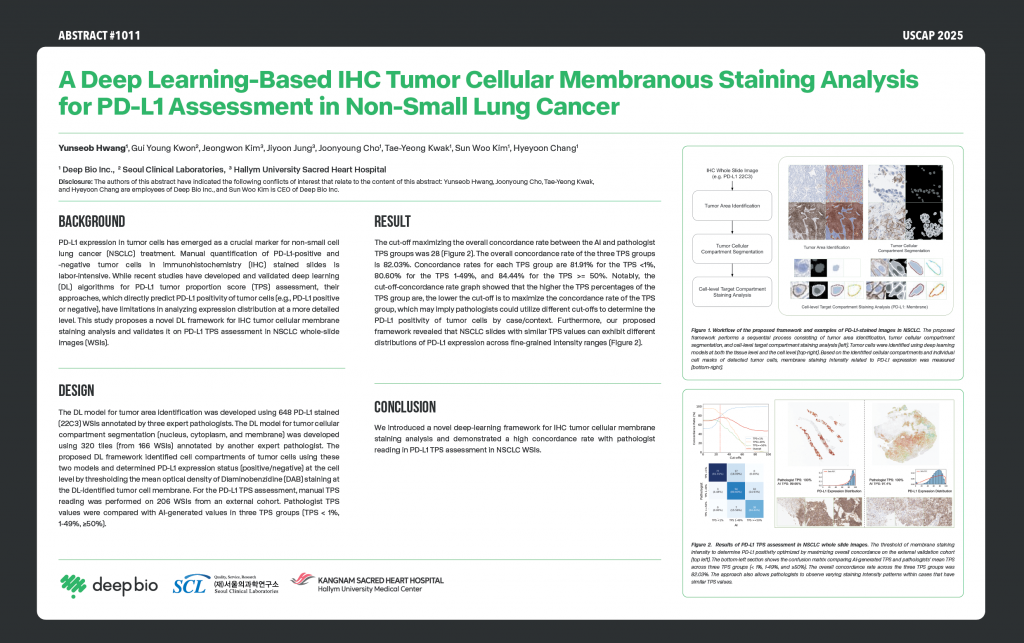
[Posters] USCAP 2025 – A Deep Learning-Based IHC Tumor Cellular Membranous Staining Analysis for PD-L1 Assessment in Non-Small Lung Cancer
Yunseob Hwang(1), Gui Young Kwon(2), Jeongwon Kim(3), Jiyoon Jung9(3), Joonyoung Cho(1), Tae-Yeong Kwak(1), Sun Woo Kim(1), Hyeyoon Chang(1)
1 Deep Bio Inc.,
2 Seoul Clinical Laboratories,
3 Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital
Disclosure: The authors of this abstract have indicated the following conflicts of interest that relate to the content of this abstract: Yunseob Hwang, Joonyoung Cho, Tae-Yeong Kwak, and Hyeyoon Chang are employees of Deep Bio Inc., and Sun Woo Kim is CEO of Deep Bio Inc.
[USCAP 2025] Transforming Cancer Detection: Deep Bio’s AI Research Featured at USCAP Annual Meeting
Insights into AI-Enhanced Diagnostic Tools for Prostate, Breast, and Lung Cancers
SEOUL, SOUTH KOREA, March 4, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ — Deep Bio, a leader in AI-driven cancer diagnostics, is excited to announce its participation in the 114th United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology (USCAP) Annual Meeting, taking place from March 22 to March 27, 2025, at the Boston Convention and Exhibition Center. The company will showcase key research findings through one platform presentation and two poster sessions, highlighting Deep Bio’s advancements in using AI to enhance diagnostic accuracy and support pathologists in clinical decision-making.
Research Highlights at USCAP:
1.Platform Presentation (Abstract #2253):
1)Title: Expansion of AI in Prostate Diagnostics: From Cancer to Atypical Large Glandular Proliferation
2)Date & Time: Monday, March 24, 2025, 8:15 a.m. – 8:30 a.m.
3)Presenting Author: Joonyoung Cho
4)Overview: This study explores an AI model extending beyond prostate cancer detection to identify atypical large glandular proliferations and perineural invasion. (The study presents a multiple instance learning (MIL) approach to refine diagnostic insights while minimizing computational overhead and annotation requirements).
2.Poster Presentation (Abstract #2257):
1)Title: Improving Breast Lesion Classification Performance Using Nuclei Information
2)Poster Board #: 35
3)Date & Time: Tuesday, March 25, 2025, 1:00 p.m. – 4:30 p.m.
4)Overview: This research examines how leveraging nuclear features within AI models can optimize breast lesion classification.
3.Poster Presentation (Abstract #1011):
1)Title: A Deep Learning-Based IHC Tumor Cellular Membranous Staining Analysis for PD-L1 Assessment in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
2)Poster Board #: 215
3)Date & Time: Wednesday, March 26, 2025, 9:30 a.m. – 12:00 p.m.
4)Overview: This study introduces a deep learning approach for assessing PD-L1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer using immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining patterns. The model is designed to support consistent tumor proportion score (TPS) evaluation and improves clinical interpretation.
“We are honored to share our latest research at USCAP 2025,” said Sun Woo Kim, CEO of Deep Bio. “Our studies demonstrate the significant strides we’ve made in applying AI to pathology, aiming to improve diagnostic precision and prediction of patient outcomes across various cancer types.”
Following USCAP, Deep Bio will also present new research at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2025, which will be held from April 25 to April 30 in Chicago, Illinois.
For more information about Deep Bio’s presentations at USCAP 2025, please visit https://2025am.uscap.org/ or schedule a meeting at booth# 511.
About Deep Bio
Founded in 2015, Deep Bio Inc. develops AI-powered solutions for cancer pathology diagnostics, utilizing advanced deep learning technologies to enhance diagnostic precision and pathologist efficiency. The company specializes in in-vitro diagnostic medical device software (IVD SaMD) that integrates data-driven insights to support clinical decision-making.
Deep Bio’s flagship AI solution, DeepDx Prostate, marked with European CE-IVD, processes Whole Slide Images (WSI) to identify and segment cancerous lesions accurately. The software provides comprehensive classification by Gleason pattern, precise tumor localization, and critical metrics such as Gleason score quantification and tumor volume assessment, essential for diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment planning.
This AI technology enables detailed analysis and reporting, supporting healthcare professionals with precise diagnostic insights. In 2024, Deep Bio was recognized for its innovation with the CES Innovation Award. The company remains committed to transforming pathology workflows and improving patient outcomes worldwide.
![[Product Introduction] DeepCDx Membrane IHC](https://deepbio.co.kr/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/thumb-2949012065_f4FSHsq0_ca04d97dcf2579261bf285cb90e0a5a0af54e263_1400x787.png)
![[Peer-Reviewed Publications] Scientific Reports – Clinical Implications of Deep Learning- Based Image Analysis of Whole Radical Prostatectomy Specimens](https://deepbio.co.kr/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/2949012065_mn7tqI3w_249209586711fde517f0bc3e58cb687efa1afe74.png)